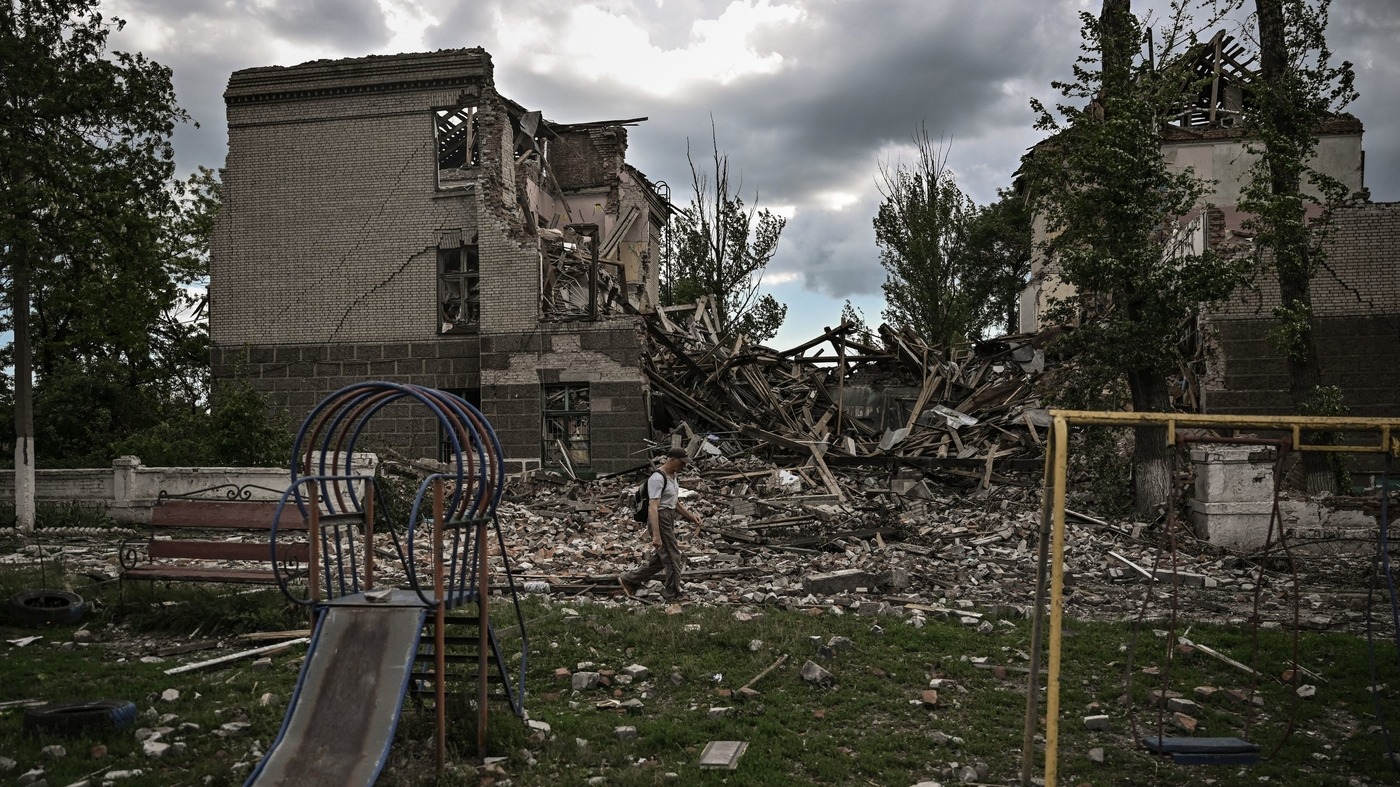
After nearly two years of conflict, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has left a devastating impact on the country’s people and economy. The war has caused staggering losses, with Ukraine’s GDP plummeting by 40% in 2022.
While there was a slight recovery in 2023, an additional 7.1 million Ukrainians now live in poverty. The human cost of the war is also immense, with estimates of civilian and military casualties reaching alarming numbers.
The UN reports approximately 10,400 civilian deaths and 19,000 wounded, while military casualties are estimated at around 70,000 soldiers killed and 100,000 wounded on both sides. Millions have been displaced from their homes, adding to the humanitarian crisis.
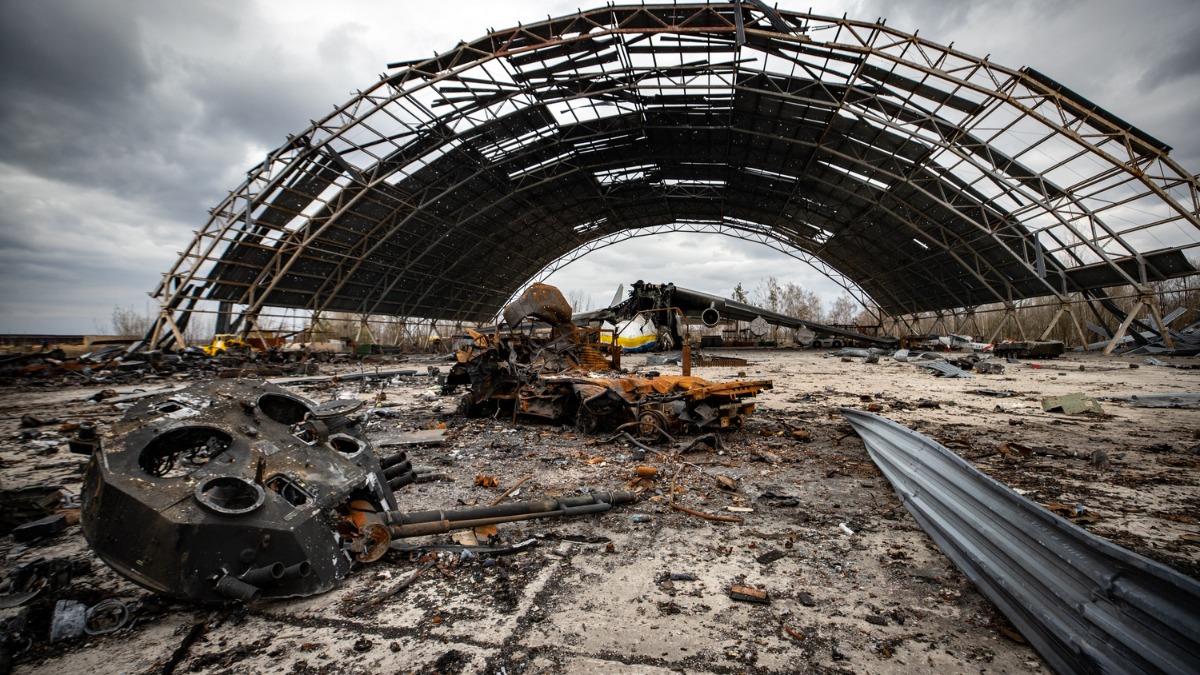

Two Years On, Ukraine (Credits: Labour Outlook)
Despite the challenges, both Ukraine and Russia have shown resilience in their ability to sustain the conflict. Ukraine’s ability to continue the war relies heavily on aid from the West, while Russia has managed to sustain its military effort through revenue from energy exports and reserves.
The stability of the Russian economy and President Putin’s anticipated reelection demonstrate the country’s ability to weather economic sanctions and continue the war effort.
On the other hand, Ukraine remains heavily dependent on support from the West, requiring at least $40 billion to sustain government services and support its population.
While the EU provides civil funding, the US is the primary source of military funding. However, Ukraine must demonstrate financial sustainability to receive assistance from the IMF and World Bank, complicating its efforts to secure loans and restructure its debt.
Despite some improvements in exports, Ukraine’s trade deficit continues to worsen, adding to its economic challenges. The country faces a daunting task of rebuilding its economy, supporting its population, and navigating complex financial issues while continuing to endure the hardships of war.