MetalMiner, identified as the largest metals-related media site in the US, offers a global perspective on the trends and issues within the metal industry. Recently, China’s steel exports have faced criticism from various countries, including the US, EU, and India. China’s struggle to balance supply and demand in its steel industry has led to a decline in crude steel production. Proposed regulations in China aim to address energy conservation and carbon emissions within the steel sector.
China’s surplus steel stockpile has become a point of concern, prompting the country to resort to exporting it to foreign markets at lower prices. President Biden has proposed triple tariffs on Chinese steel imports in response to this issue. Other countries such as the EU, India, Thailand, Mexico, and Brazil have also expressed dissatisfaction with China’s steel export tactics, with some implementing tariffs on Chinese steel imports.
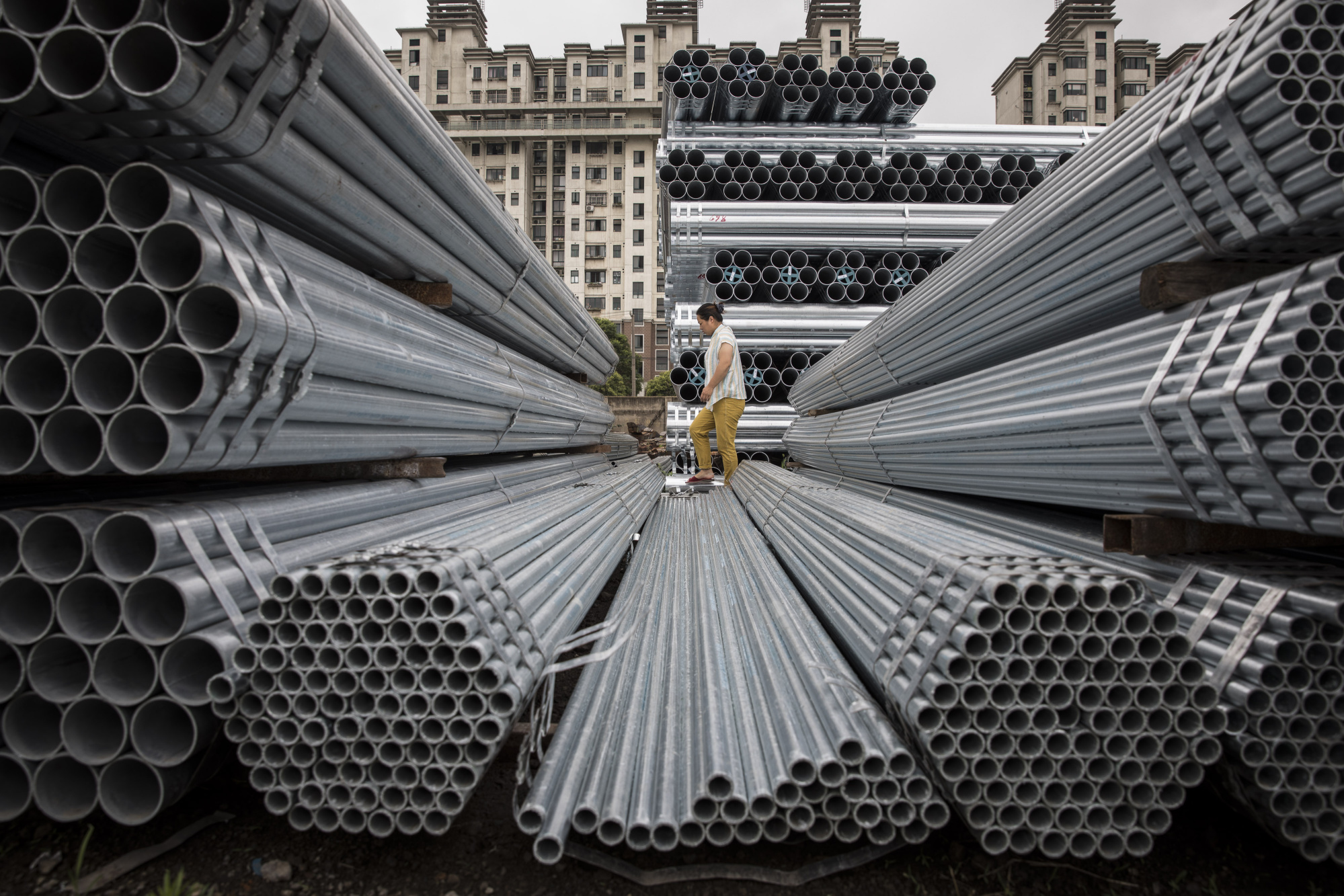

China’s Steel Trading Faces Questions with Rising Demand (Credits: Bloomberg)
Despite a decline in China’s crude steel production, iron ore imports and domestic production have increased. The World Steel Association forecasts a 1.7% increase in global steel demand for the current year. China’s National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) plans to collaborate with stakeholders to regulate crude steel production, focusing on energy conservation and carbon emissions reduction.
The Chinese steel industry faces challenges as domestic demand contracts and steel production is capped to reduce carbon emissions. Despite the US and other countries’ discontent with China’s steel export practices, analysts believe that major export markets like the Middle East and Japan will continue unaffected by the US’s stance.