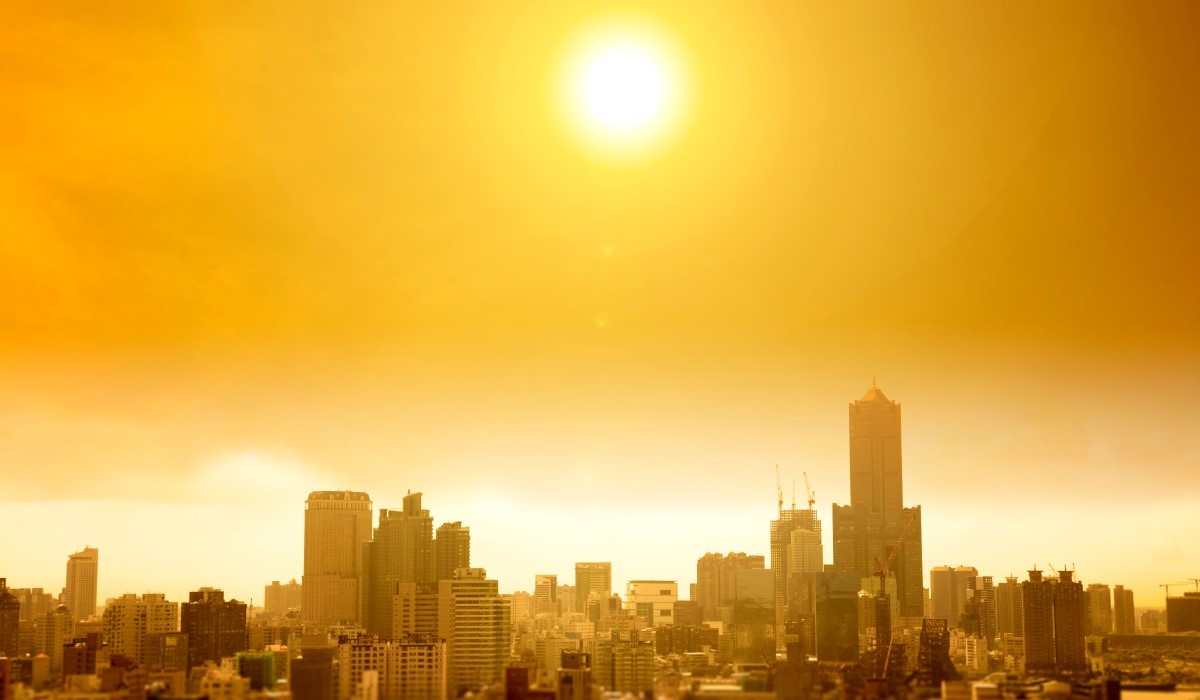
The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) has launched new initiatives to address the increasing threat of severe heat across the nation. HUD unveiled a dedicated webpage focused on Extreme Heat, serving as a comprehensive resource hub for communities to prepare and respond to extreme heat events. This marks the first time HUD has taken such a step, indicating a heightened awareness of the issue’s significance.
Included in HUD’s initiatives are two technical assistance products: an “extreme heat quick guide” aimed at assisting communities in planning and implementing mitigation strategies, and a webinar specifically addressing the challenges posed by extreme heat and cold. Additionally, HUD plans to host a stakeholder briefing on May 23 to further delve into the topic and engage with key stakeholders.
Adrianne Todman, HUD’s acting secretary, emphasized the broad impact of extreme heat, particularly on historically underserved communities. The department’s priority is to raise awareness about the dangers associated with extreme heat and to provide support to local and state leaders as they navigate this climate hazard.

HUD’s Mission: Safeguarding Communities Against Extreme Heat (Credits: UPI)
HUD is part of a collaborative effort involving over 20 federal agencies to establish a National Integrated Heat Health Information System. This initiative aims to increase awareness of extreme heat’s risks and develop solutions to mitigate its adverse effects on communities nationwide.
The effects of extreme heat, exacerbated by climate change, are increasingly evident in the housing market. Data from Redfin indicates significant population shifts towards areas prone to flooding, wildfires, and excessive heat. These trends have led to elevated home prices in such areas, reflecting a growing awareness of climate-related risks among homebuyers.
Climate risks, including those related to extreme heat, are also impacting home insurance costs. Redfin’s chief economist, Daryl Fairweather, highlighted how rising insurance premiums and considerations about climate risks are influencing people’s decisions about where to live. This underscores the growing importance of climate resilience in the housing market and the need for proactive measures to address these challenges.